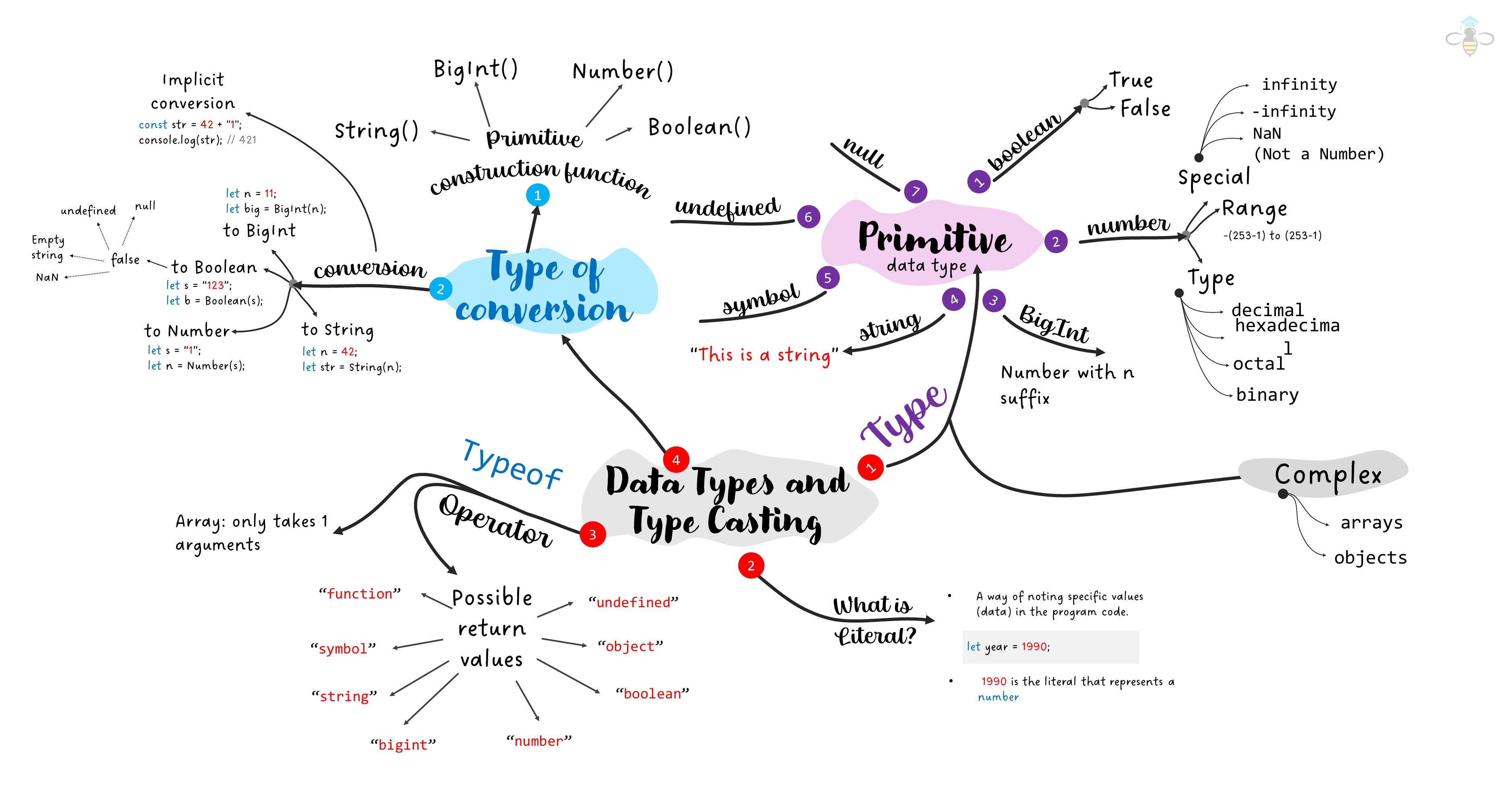
7. Type Casting in JavaScript
7.1 Primitive Construction Functions
JavaScript provides primitive construction functions for explicit type conversion.
let numberAsString = String(42);
let stringAsNumber = Number("42");
let truthyValue = Boolean("Hello");
let falseyValue = Boolean(0);
7.2 Conversion Examples
let numericString = "123";
let numericValue = Number(numericString);
console.log(numericValue); // Outputs: 123 (converted from string to number)
let booleanValue = Boolean("true");
console.log(booleanValue); // Outputs: true (converted from string to boolean)
let stringRepresentation = String(42);
console.log(stringRepresentation); // Outputs: "42" (converted from number to string)
let bigIntAsString = "9007199254740992";
let bigIntValue = BigInt(bigIntAsString);
console.log(bigIntValue); // Outputs: 9007199254740992n (converted from string to BigInt)
7.3 Implicit Type Conversion
JavaScript also performs implicit type conversion, where the interpreter automatically converts one data type to another, depending on the context.
let result = "5" + 5;
console.log(result); // Outputs: "55" (implicit conversion, concatenating a string and a number)
Understanding these fundamental concepts of data types and type casting in JavaScript is crucial for writing robust and efficient code. Whether dealing with primitive data types, literals, the typeof operator, or type conversions, a solid grasp of these concepts will enhance your ability to work with data effectively in JavaScript.